Future Factory Website Documentation
Over here you can find the documentation for the Future Factory website.
If you are looking for an user manual and not code specific documentation, then take a look at this pdf.
The website is written in Python using the Django framework. At the moment Tom Meulenkamp from RoboTeam Twente is the lead maintainer on this website and is also responsible for hosting it. However, this should not discourage other people from wanting to help and work on this site.
The code structure attempts to make it easy to search through and is written in a way that should not be too complex for someone with some experience with the Django framework.
Although the code has some documentation incorporated into it, this documentation will focus more on the general picture allowing one to understand on how all of these components work together.
Table of Contents
General Information
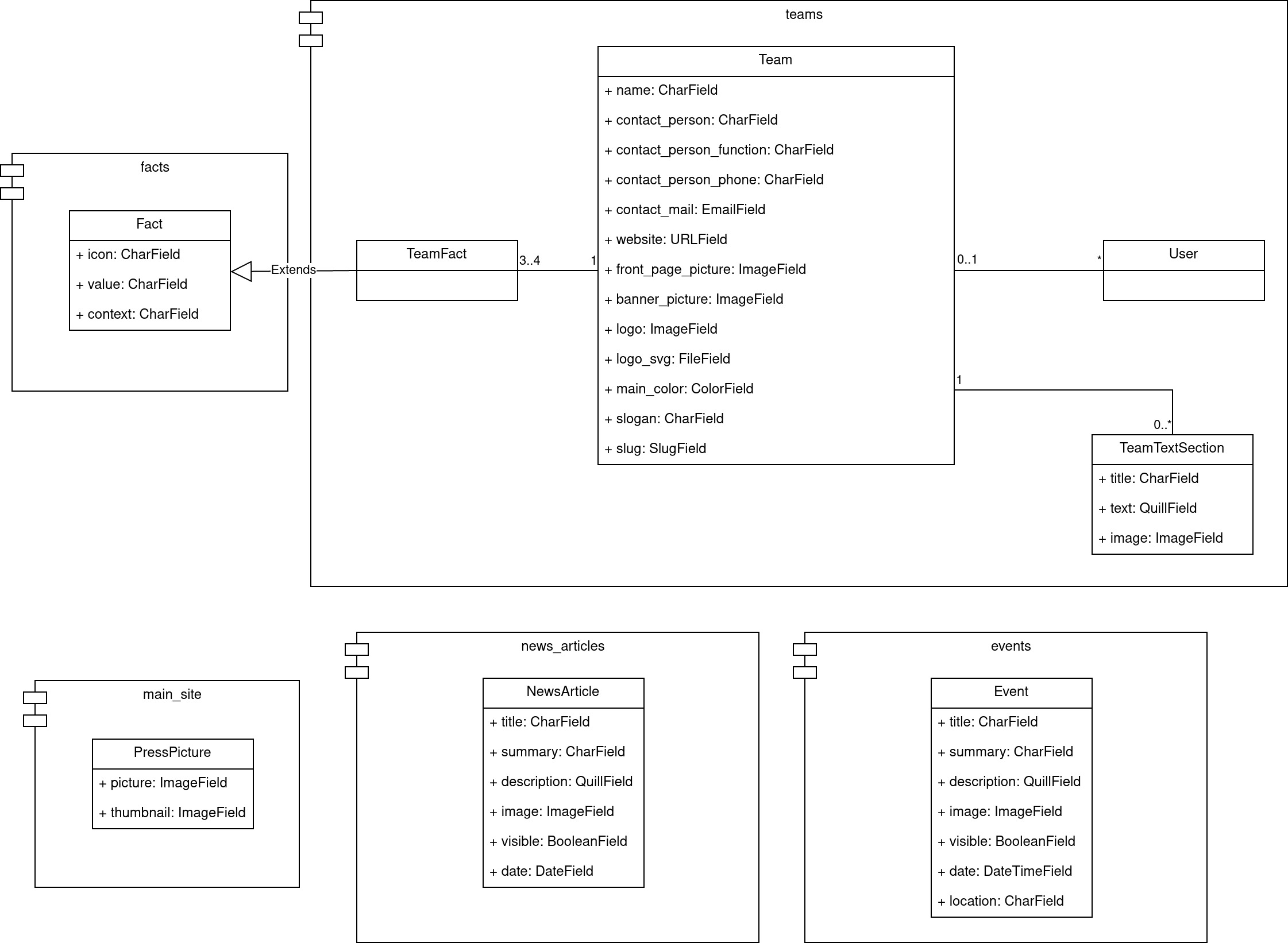
Most entities have their own module (also known as app) within this project. This allows for a clear distribution between models, views and other stuff.
Class Diagram
Templates
Each page that one sees is built with the Django template system.
Every page extends the basis.html template that can be found in /templates. This template handles the basis HTML
structure such as meta tags, favicons, the navigation bar and the footer. Each template then
inherits this basic template and
is able to fill out the following blocks:
- description
- Contains a short description about this specific page. This will be shown in the Google search results.
- title
- The title of the current page.
- head
- Additional HTML that should go into the head, for example additional stylesheets.
- Also, these blocks usually contain additional CSS, for example to override the default background picture in the header.
- nav_bar
- By default the navigation bar only contains the logo and home button. Any additional buttons should be added with
the following HTML:
<li class="nav-item"> <a class="nav-link" href="_link_location_">Nav item</a> </li>
- By default the navigation bar only contains the logo and home button. Any additional buttons should be added with
the following HTML:
- content
- The actual contents of this page. This will mainly contain
<section>elements.
- The actual contents of this page. This will mainly contain
- scripts
- Any JavaScript that should be loaded into the page, this will be placed after the
</body>tag.
- Any JavaScript that should be loaded into the page, this will be placed after the
Error pages
If a page cannot be found or the server raises an uncaught exception, the user will see an error message. The templates
for these pages can be found in /templates and are named according to their HTTP error codes.
Automated image compression
Images are automatically compressed, allowing for quick load times and an overall responsive website. This compression
happens on each image field that is defined somewhere in model. This compressing happens on the fly when a model is
being created or updated. The compress function can be found in future_factory_website/utils.py.
Note: When using the compress function on an optional ImageField make sure to check if an image is actually
selected. The compress cannot handle empty fields. Checking this is done as follows:
class ExampleModel(models.Model):
image = models.ImageField(null=True, blank=True)
def save(self, *args, **kwargs):
# Check if we actually have selected an image.
if self.image:
self.image = compress(self.image)
super(self).save(*args, **kwargs)